A car’s suspension is a vital system comprising various components designed to enhance stability, ensure a comfortable ride, and optimize handling. It is part of the vehicle’s skeleton beneath, absorbing road shocks, vibrations, and uneven terrain to ensure a safe and pleasant journey.
Typical car suspension systems can manage substantial force, with a sedan’s front suspension supporting around 900kg to 1,500kg. On rough roads, suspensions can undergo hundreds of adjustments per minute, ensuring a consistently smooth ride. Suspension systems can influence a vehicle’s fuel efficiency by reducing drag and improving aerodynamics, resulting in fuel savings.
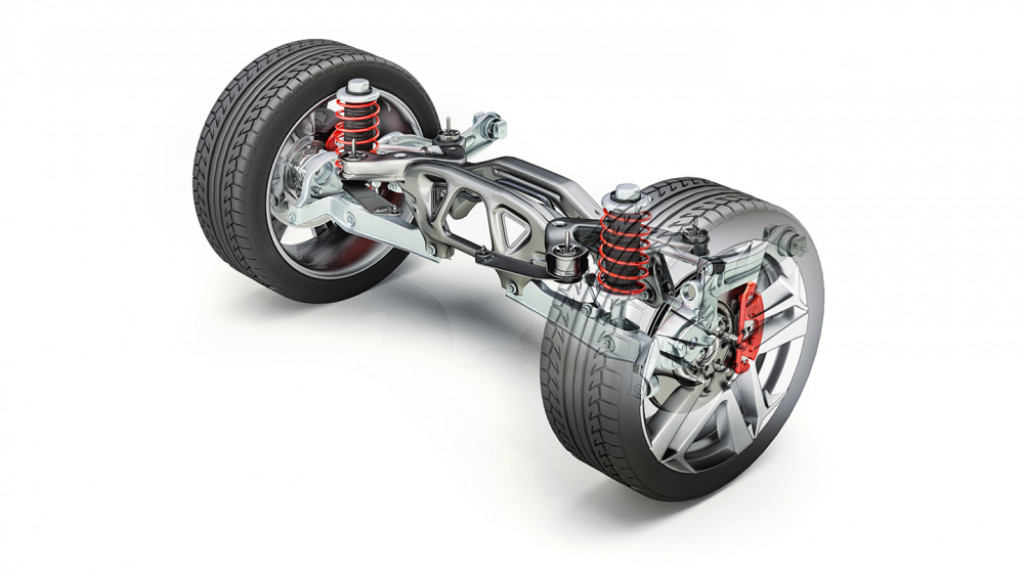

Before we jump into everything there is to know about a car’s suspension, here is a beginner’s guide to car terms that you need to know.
Car Suspension History
In the early days of the automobile, suspension systems were either rudimentary or non-existent. Vehicles rode on solid metal or wooden wheels, offering little to no cushioning against rough roads. As cars evolved, leaf springs and solid axles became common suspension components. Leaf springs provided some flexibility and shock absorption, while solid axles allowed for relative movement between the wheels.
1930s: Independent Front Suspension:
Independent front suspensions enhanced handling and comfort.
1940s – 1950s: Coil Springs and Hydraulics:
Coil springs and hydraulic shocks improve ride quality.
1950s – 1960s: Air Suspension and Electronics:
Air suspension and electronics introduced adjustable ride height.
Late 20th Century – Present: Modern Developments:
Advanced materials and computer control enhance comfort and handling.
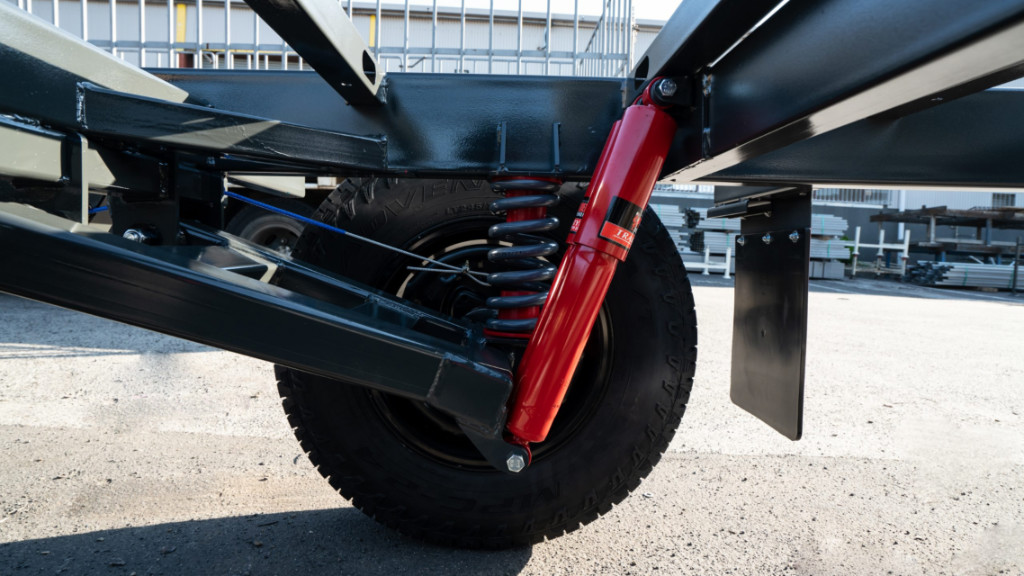

What Are The Advantages Of Having A Suspension?
Having a vehicle suspension offers numerous benefits, making rides safer, more comfortable, and better handling. A well-designed suspension system is vital for a vehicle’s performance and safety. It elevates comfort, stability, handling, and safety while extending tyre life, resulting in a more enjoyable and efficient driving experience. Here are the key advantages:
- Enhanced Comfort: Suspension systems absorb road shocks, providing a smoother ride by reducing bumps and vibrations.
- Improved Stability: Maintaining tyre contact with the road enhances stability, even on uneven surfaces and during turns.
- Better Handling: Well-designed suspension offers precise steering and responsiveness, aiding vehicle control, especially during quick manoeuvres.
- Reduced Tyre Wear: Properly functioning suspension distributes weight evenly, extending tyre life and saving on replacements.
- Safer Braking: Stable suspension ensures all tyres maintain contact, improving braking performance and reducing stopping distances.

- Reduced Driver Fatigue: A comfortable, less jolting ride prevents driver fatigue on long trips, promoting safety.
- Adaptability: Adjustable suspension allows drivers to customise ride height and stiffness, enhancing off-road capability and highway comfort.
- Load Handling: Suspension systems adapt to varying loads, ensuring vehicle stability when carrying passengers or cargo, crucial for trucks and SUVs.
- Off-Road Capability: Robust suspension enables off-road vehicles to tackle rough terrain, absorb shocks, and maintain traction.
- Reduced Vehicle Noise: By isolating road impacts, suspension systems create a quieter cabin for a more pleasant driving environment.
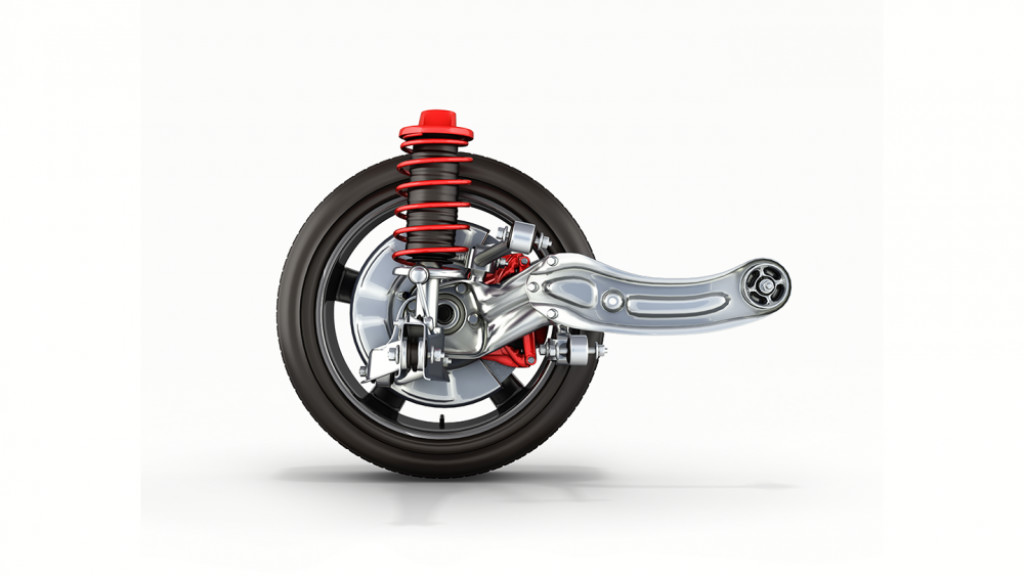

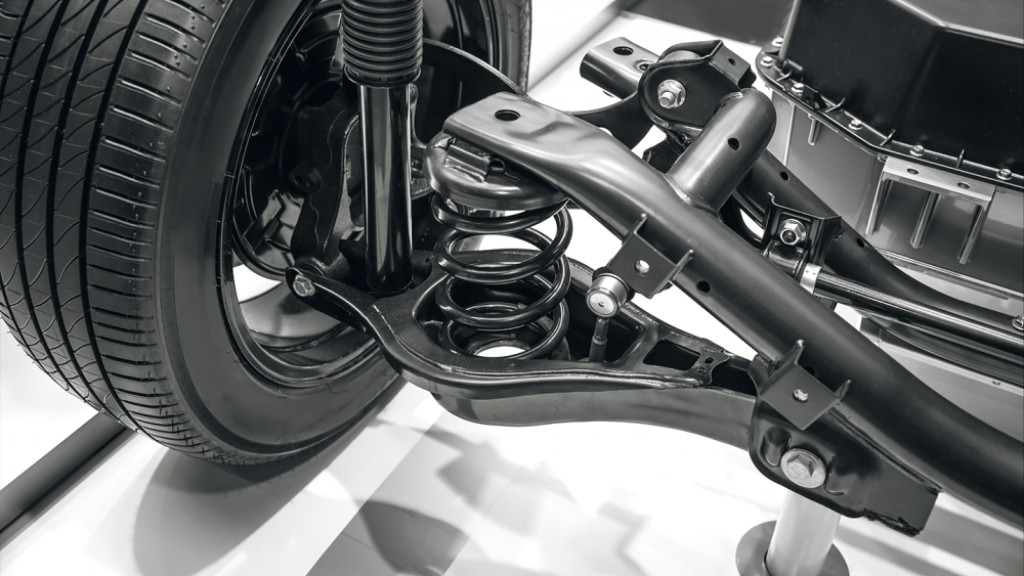
Different Components In A Suspension
A vehicle’s suspension system comprises various components that collaborate to deliver a smooth, controlled ride while upholding stability and handling. Here are the key components:
- Springs: These absorb road shocks, with coil springs and leaf springs being common types.
- Shock Absorbers (Dampers): They work alongside springs to control suspension motion, maintaining tire-road contact.
- Struts: Similar to shock absorbers but with added structural elements, commonly found in front suspension.
- Control Arms: Link the vehicle’s frame to suspension parts, controlling wheel movement and alignment.
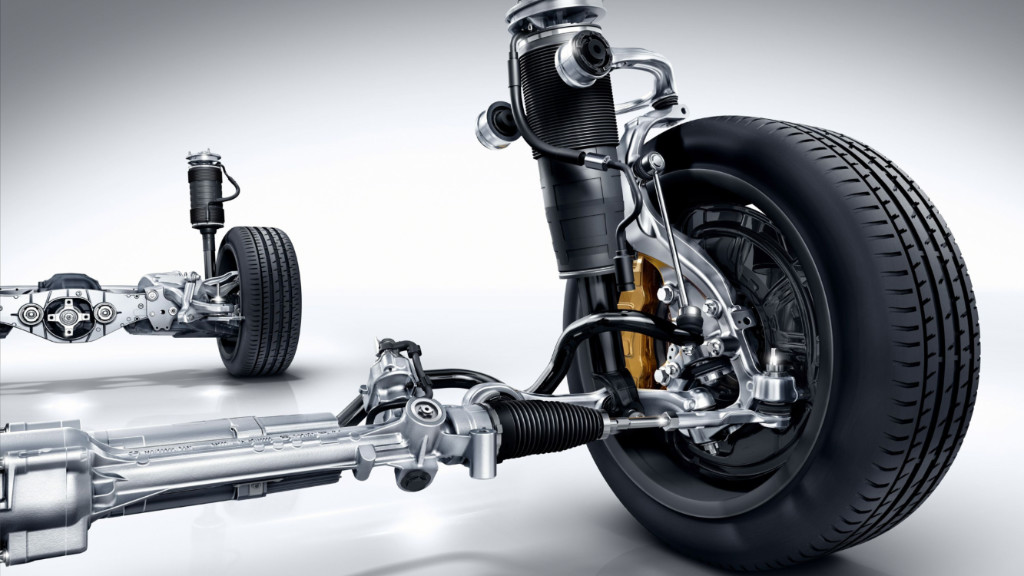

- Anti-roll Bars (Sway Bars): Metal rods connecting suspension components, reducing body roll during turns.
- Bushing: Small rubber or polyurethane parts connecting and isolating suspension elements, reducing vibrations and noise.
- Control Arm Bushing: Located at control arm connection points, allowing controlled movement while minimizing vibration and noise.
- Ball Joints: Connect control arms to steering knuckles, enabling pivoting movement and crucial for steering.
- Tie Rods & Tie Rod Ends: Part of the steering system, connecting steering linkage to wheels, aiding in steering control.
- Alignment Components: Include camber and toe adjustment arms to ensure proper wheel alignment, impacting tire wear and handling.
Types Of Car Suspension
Various types of car suspension systems are designed to meet specific driving needs and vehicle characteristics. Here are some common types:
Independent Suspension:
In this setup, each wheel can move independently, providing better handling and a smoother ride. It’s commonly used in passenger cars and modern vehicles.
Dependent Suspension:
Both wheels on an axle move together in this type. A common example is the solid rear axle suspension, seen in trucks and some older SUVs. It’s rugged but may provide a less comfortable ride compared to independent suspension.
Leaf Spring Suspension:
Consisting of stacked steel spring layers, leaf springs are often used in the rear suspension of trucks and some SUVs for robust load-carrying capacity. Usually used in heavy-duty loads.
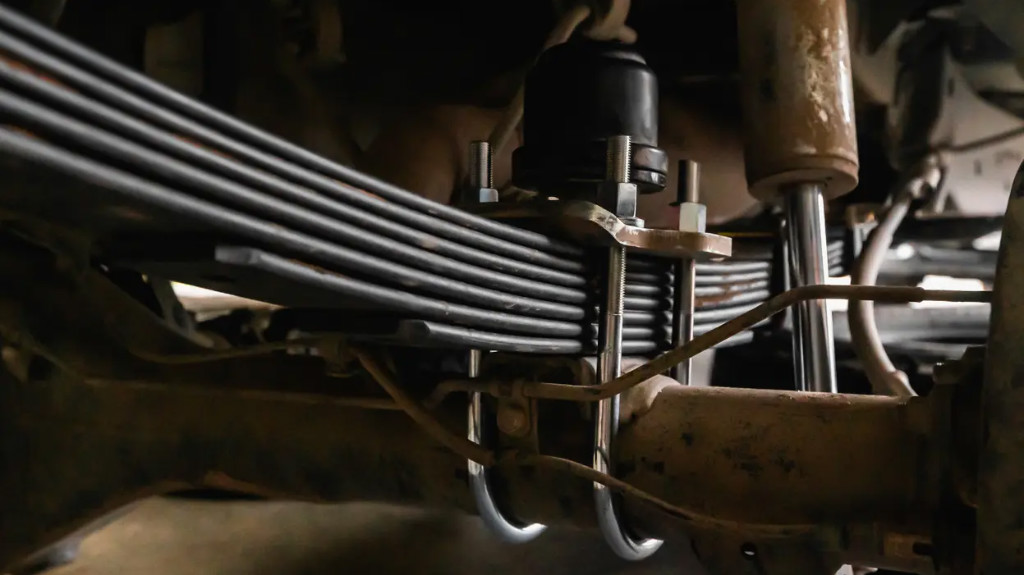

Torsion Bar Suspension:
Steel bars twist to provide spring-like resistance, less common in modern vehicles but used in some trucks and SUVs.
MacPherson Strut Suspension:
This design combines a shock absorber and coil spring into a single unit, commonly used in the front suspension of many vehicles for its simplicity and space-saving design.
Double Wishbone Suspension (A-Arm):
Two A-shaped control arms per wheel provide precise wheel movement control. Often found in sports cars and performance-oriented vehicles.
Multi-Link Suspension:
This system uses multiple control arms and links, offering a balance between ride comfort and handling. It’s common in luxury cars and some SUVs.
Air Suspension:
Air springs replace traditional springs, allowing adjustable ride height and stiffness. It offers a comfortable and adaptable ride, often used in luxury vehicles and SUVs.
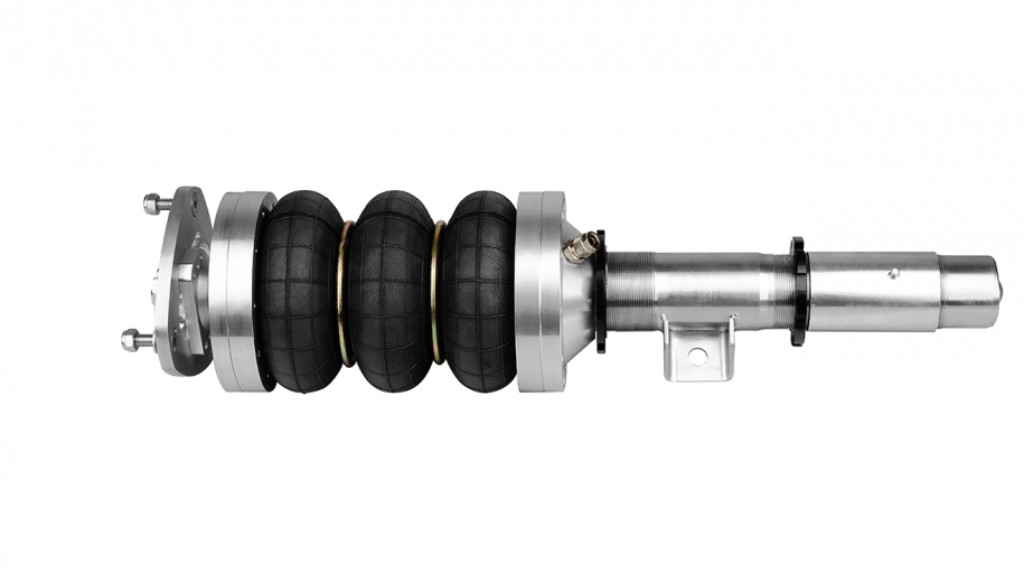
Hydraulic Suspension:
Pressurized hydraulic fluid controls ride height and damping. While offering a smooth, adjustable ride, it’s less common in modern vehicles.
Semi-Active Suspension:
These systems offer adjustable damping rates without the complexity of fully active systems, striking a balance between comfort and performance.
Active Suspension:
Using electronic sensors and actuators, active suspension systems continuously adjust stiffness and ride height. They adapt to various driving conditions for improved comfort and handling.
What Is A Suspension Setup?
A suspension setup, also known as a suspension configuration or arrangement, refers to the specific combination and tuning of components within a vehicle’s suspension system. It is tailored to achieve a particular balance between ride comfort, handling, and performance characteristics based on the vehicle’s intended use and design goals. Manufacturers and enthusiasts often fine-tune suspension setups to optimize a vehicle’s performance for specific driving conditions or preferences.
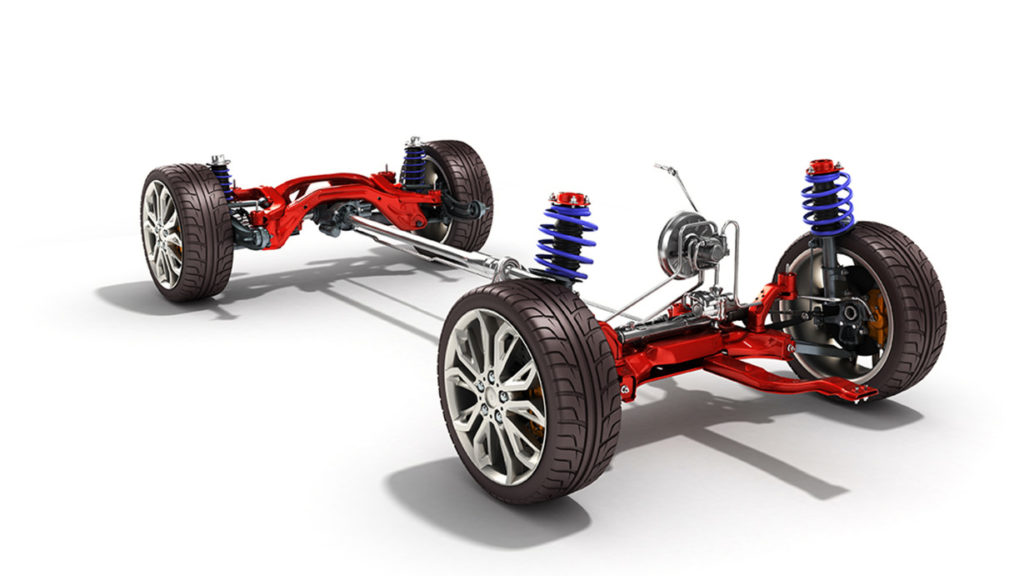

Different Types Of Suspension Setups
There are several different types of suspension setups, each tailored to specific purposes and vehicle characteristics. Here are some common types of suspension setups:
Comfort-Oriented Suspension:
These setups prioritize a smooth and comfortable ride over aggressive handling. They typically feature softer springs and shock absorbers, resulting in a cushioned ride quality. Such suspension is commonly found in luxury cars and family sedans.
Performance Suspension:
Designed for sportier driving and enhanced handling, performance suspension systems feature stiffer springs and shock absorbers. They offer improved responsiveness and reduced body roll during cornering. Sports cars and sport-tuned variants often employ this setup.
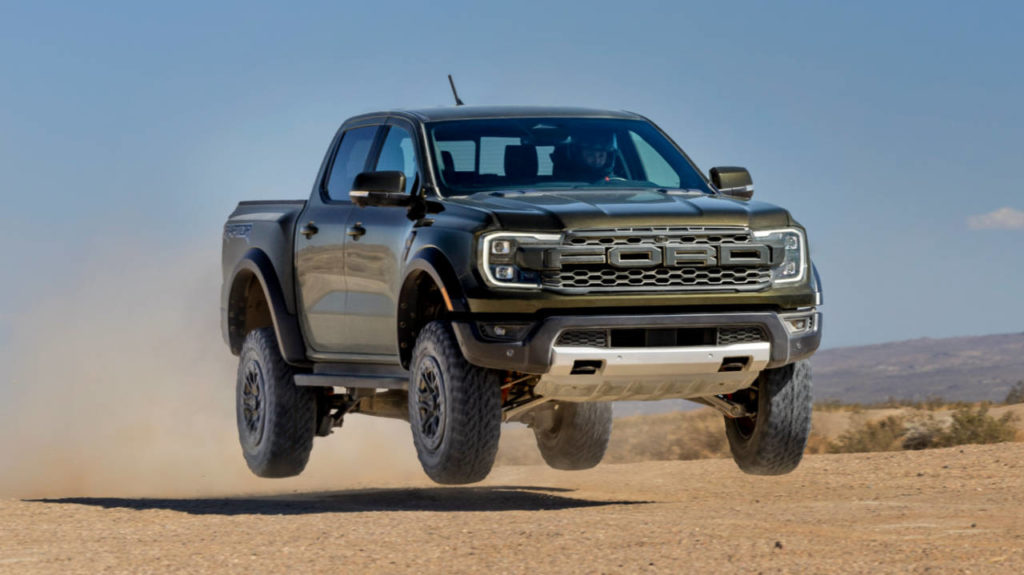

Raised Suspension:
Off-road suspension systems are designed for rugged terrain and uneven surfaces. They typically have longer suspension travel, heavy-duty components, and increased ground clearance. Off-road vehicles like trucks and SUVs commonly use this setup.
Lowered Suspension (Lowering Kit):
Lowered suspension reduces the vehicle’s ride height, which can improve aerodynamics and create a sportier appearance. They often feature shorter springs or adjustable components. Enthusiasts who want a more aggressive look and better handling may opt for this setup.
That was your complete guide on the suspension of a car. We will be posting detailed blogs on other components of a car. Keep an eye on the DubiCars Blog section for more such guides.
Looking to own a car? Here is a list of used cars on sale in the UAE and new cars on sale in the UAE.
Other Automotive Guides:
The post Get To Know Your Car Better: A Detailed Guide To Automotive Terms — Suspension appeared first on Dubi Cars - New and Used Cars.
from Dubi Cars – New and Used Cars https://ift.tt/hmE12zd
https://ift.tt/Q4tF3j5